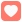
( )是科学研究的基本方法,其主要特点就是采取规范的方法收集实际材料、数据、事实,再从这些材料、数据、事实中归纳出普遍性的结论来。
A. 实证研究 B. 理论研究 C. 作品分析法 D. 实验法
点击查看答案
Researchers at the University of Arizona, led by Teresa Cummins, conducted an exploratory study on the online learning modules, designed to supplement hands-on classes taught by local experts and supported by an overview text, to help users increase their understanding of key concepts in the Arizona Master Watershed Steward program. They also sought to determine whether program participants would use the non-compulsory modules. Their evaluation revealed that module users increased their understanding of key watershed concepts; participants in the evaluation demonstrated a 30 percent increase in content knowledge following module use. Additionally, 70 percent of participants retained this knowledge through a two-month follow-up test. A follow-up survey showed that approximately half of the participants returned to the online modules on their own; several of these users returned several times and spent multiple hours per session. Comments from the follow-up survey suggested that the users accessed the site either as they had the time or as they needed the information. Online usage statistics indicated participants continued to visit the site for many months following the modules’ release and advertisement. Though many visits were very brief (a single pageview; only a couple of seconds), visitors with many returns to the site and/or long visits appeared to be working through the modules. One participant stated, "My brain can only hold so much information; the modules keep information on-hand." Other participants commented that the modules were "more interesting and interactive" than the text material, and a "very effective tool" and "a great resource to the Master Watershed Steward community." The Arizona Master Watershed Steward program, sponsored by University of Arizona, prepares adults to serve as volunteers in the conservation of water resources and the protection, restoration, and monitoring of their watersheds. The modules were intended to reinforce concepts covered in classes and further engage participants in the learning process. One key finding was that the modules were not clearly preferred by users over in-person instruction. One participant stated, "For me, they are just another avenue for learning, a supplement or additional reference. I prefer in person and real hands-on learning." Other participants similarly expressed their desire for hands-on and face-to-face interaction. Several participants noted that the usefulness of in-person lectures—was a function of the presenter. Overall, the exploratory evaluation indicated that the modules were a welcome supplement to the course and were effective in reinforcing key concepts. Participants retained knowledge for several weeks, although since subjects were self-selected, they may have been self-motivated to pay attention and master the online module materials. "I am constantly searching for new ways to educate our program’s diverse audiences and reinforce watershed science concepts, " says Candice Rupprecht, state coordinator for the Master Watershed Steward program. "I am excited to know that online learning modules can enhance our program by offering additional independent learning opportunities for our volunteers.
Researchers at the University of Arizona, led by Teresa Cummins, conducted an exploratory study on the online learning modules, designed to supplement hands-on classes taught by local experts and supported by an overview text, to help users increase their understanding of key concepts in the Arizona Master Watershed Steward program. They also sought to determine whether program participants would use the non-compulsory modules.
Their evaluation revealed that module users increased their understanding of key watershed concepts; participants in the evaluation demonstrated a 30 percent increase in content knowledge following module use. Additionally, 70 percent of participants retained this knowledge through a two-month follow-up test.
A follow-up survey showed that approximately half of the participants returned to the online modules on their own; several of these users returned several times and spent multiple hours per session. Comments from the follow-up survey suggested that the users accessed the site either as they had the time or as they needed the information.
Online usage statistics indicated participants continued to visit the site for many months following the modules’ release and advertisement. Though many visits were very brief (a single pageview; only a couple of seconds), visitors with many returns to the site and/or long visits appeared to be working through the modules.
One participant stated, "My brain can only hold so much information; the modules keep information on-hand." Other participants commented that the modules were "more interesting and interactive" than the text material, and a "very effective tool" and "a great resource to the Master Watershed Steward community."
The Arizona Master Watershed Steward program, sponsored by University of Arizona, prepares adults to serve as volunteers in the conservation of water resources and the protection, restoration, and monitoring of their watersheds. The modules were intended to reinforce concepts covered in classes and further engage participants in the learning process.
One key finding was that the modules were not clearly preferred by users over in-person instruction. One participant stated, "For me, they are just another avenue for learning, a supplement or additional reference. I prefer in person and real hands-on learning." Other participants similarly expressed their desire for hands-on and face-to-face interaction. Several participants noted that the usefulness of in-person lectures—was a function of the presenter.
Overall, the exploratory evaluation indicated that the modules were a welcome supplement to the course and were effective in reinforcing key concepts. Participants retained knowledge for several weeks, although since subjects were self-selected, they may have been self-motivated to pay attention and master the online module materials.
"I am constantly searching for new ways to educate our program’s diverse audiences and reinforce watershed science concepts, " says Candice Rupprecht, state coordinator for the Master Watershed Steward program. "I am excited to know that online learning modules can enhance our program by offering additional independent learning opportunities for our volunteers.
点击查看答案
 题目内容
(请给出正确答案)
题目内容
(请给出正确答案)
 参考答案
参考答案
 十点题库官方参考答案
(由十点题库聘请的专业题库老师提供的解答)
十点题库官方参考答案
(由十点题库聘请的专业题库老师提供的解答)