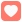
患者女性,40岁。车祸伤后1小时,伤后昏迷入院。查体:GCS 7分,瞳孔左︰右=4mm︰2mm,左侧对光反应消失,右侧肢体偏瘫。BP 170/100mmHg,HR 60次/分,R 12次/分。针对
A.5cm,考虑受伤出血的机制为A、左额、颞部位的冲击伤所致
B、左额、颞部位的加速性损伤所致
C、左枕部的加速性损伤所致
D、右枕部的减速性损伤所致
E、以上均正确
点击查看答案
Why does cream go bad faster than butter Some researchers think they have the answer, and it comes down to the structure of the food, not its chemical composition—a finding that could help rid some processed foods of chemical preservatives. Cream and butter contain pretty much the same substances, so why cream should sour much faster has been a mystery. Both are emulsions—tiny globules (小球) of one liquid evenly distributed throughout another. The difference lies in what’s in the globules and what’s in the surrounding liquid, says Brocklehurst, who led the investigation. In cream, fatty globules drift about in a sea of water. In butter, globules of a watery solution are locked away in a sea of fat. The bacteria which make the food go bad prefer to live in the watery regions of the mixture. "This means that in cream, the bacteria are free to grow throughout the mixture," he says. When the situation is reversed, the bacteria are locked away in compartments (密封) buried deep in the sea of fat. Trapped in this way, individual colonies cannot spread and rapidly run out of nutrients. They also slowly poison themselves with their waste products. "In butter, you get a self-limiting system which stops the bacteria growing," says Brocklehurst. The researchers are already working with food companies keen to see if their products can be made resistant to bacterial attack through alterations to the food’s structure. Brocklehurst believes it will be possible to make the emulsions used in salad cream, for instance, more like that in butter. The key will be to do this while keeping the salad cream liquid and not turning it into a solid lump.
Why does cream go bad faster than butter Some researchers think they have the answer, and it comes down to the structure of the food, not its chemical composition—a finding that could help rid some processed foods of chemical preservatives.
Cream and butter contain pretty much the same substances, so why cream should sour much faster has been a mystery. Both are emulsions—tiny globules (小球) of one liquid evenly distributed throughout another. The difference lies in what’s in the globules and what’s in the surrounding liquid, says Brocklehurst, who led the investigation.
In cream, fatty globules drift about in a sea of water. In butter, globules of a watery solution are locked away in a sea of fat. The bacteria which make the food go bad prefer to live in the watery regions of the mixture. "This means that in cream, the bacteria are free to grow throughout the mixture," he says.
When the situation is reversed, the bacteria are locked away in compartments (密封) buried deep in the sea of fat. Trapped in this way, individual colonies cannot spread and rapidly run out of nutrients. They also slowly poison themselves with their waste products. "In butter, you get a self-limiting system which stops the bacteria growing," says Brocklehurst.
The researchers are already working with food companies keen to see if their products can be made resistant to bacterial attack through alterations to the food’s structure. Brocklehurst believes it will be possible to make the emulsions used in salad cream, for instance, more like that in butter. The key will be to do this while keeping the salad cream liquid and not turning it into a solid lump.
点击查看答案
 题目内容
(请给出正确答案)
题目内容
(请给出正确答案)
 参考答案
参考答案
 十点题库官方参考答案
(由十点题库聘请的专业题库老师提供的解答)
十点题库官方参考答案
(由十点题库聘请的专业题库老师提供的解答)